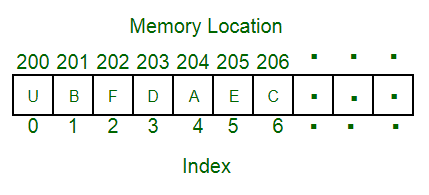
In the Numpy definition, you read that they basically work with Arrays so what are Arrays???
- An array is a collection of items stored at continuous memory locations.
- All the stored items should be of same type.
Arrays are of two types:
- One-Dimensional Array
- Multi-Dimensional Array
A one-dimensional array (or single dimension array) is a type of linear array.Accessing its elements involves a single subscript which can either represent a row or column index. Example:
# A character array in C/C++/Java
char arr1[] = {'D','e','v','I','n','c','e','p','t'};
# An Integer array in C/C++/Java
int arr2[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
To access the elements of a single-dimensional Array you can use the indexes and most of the Arrays are zero-indexed.
arr1[0]; # gives us D
arr1[2]; # gives us v
arr2[1]; # gives us 20
arr2[4]; # gives us 50
Note: Array of characters is called a string. Yes!! These are the same strings which we use in Pyhton they are also Arrayss hidden in plain sight.
A multi-dimensional array is an array with more than one level or dimension. For example, a 2D array, or two-dimensional array. Meaning it is a matrix of rows and columns (think of a table).
You can access elements in a multi-dimensional like in the example showed above..
Few simple Examples:
list=['DevIncept',10,'Sam',100,20]
print(list[0])
print(list[2])
print(list[3])A Python list may contain different types! Indeed, you can store a number, a string, and even another list within a single list. Result:
DevIncept
Sam
100You can tinker with the above example in the provided Jupyter Notebook..
Note:
All of the elements in a NumPy array should be homogeneous.
To create a basic NumPy Array you can use the function np.array() The array object in NumPy is called ndarray
import numpy as np
arr1=np.array([1,2,3])
arr2=np.array(['a','b','c','d','e'])
arr3= np.array((1, 2, 3, 4, 5)) # You can also pass a tuple to creat an Array
print(arr1)
print(arr2)
print(arr3)
print(type(arr1))Result:
[1 2 3]
['a' 'b' 'c' 'd' 'e']
[1 2 3 4 5]
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>Besides the above examples you can create Arrays using builtin function
- To create an Array of Zeroes use np.zeros()
- To create an Array of Ones use np.ones()
- To create an Array with a range of elements use np.arange()
import numpy as np
a=np.zeros(3)
b=np.ones(5)
c=np.arange(10)
d=np.arange(2,9) # To specify start and stop
e=np.arange(1,10,2) # To specify start and stop with step size
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
print(d)
print(e)Result:
[ 0. 0. 0.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
[2 3 4 5 6 7 8]
[1 3 5 7 9]You can try the code yourself in the provided Jupyter Notebook
- An array class in Numpy is called as ndarray.
- Number of dimensions of the array is called rank of the array.
Lets Create a 2-D(Dimensional) Array
- They are like a matrix or you can say a table
import numpy as np
arr1=np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
arr2=np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]])
arr3=np.array([['a','b','c'],['d','e','f']])
#creates a 3X3 array with all zeros
zeros=np.zeros((3,3))
#creates a 2X2 array with all ones
ones=np.ones((2,2),dtype='int64') #specify the type with (dtype) parameter
print(arr1)
print(arr2)
print(arr3)
print(zeros)
print(ones)Result:
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]
[7 8 9]]
[['a' 'b' 'c']
['d' 'e' 'f']]
# 3X3 Matrix
[[ 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0.]]
# 2X2 Matrix
[[1 1]
[1 1]]NumPy provides some cool methods you can check the number of dimensions using ndim
import numpy as np
a = np.array(42)
b = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
c = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
d = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]])
print(a.ndim)
print(b.ndim)
print(c.ndim)
print(d.ndim)Result:
0
1
2
3You can also do basic arthemetic operations with arrays.
import numpy as np
arr1=np.array([5,5,5,5])
arr2=np.array([3,3,3,3])
c=arr1+arr2
d=arr1-arr2
e=arr1/arr2
print(arr1)
print(arr2)
print(c) # addition
print(d) # subtraction
print(e) # division
print("Adding one to all elements:",c+1)
print("Subtracting one from all elements:",d-1)Result:
[5 5 5 5]
[3 3 3 3]
[8 8 8 8]
[2 2 2 2]
[1.66666667 1.66666667 1.66666667 1.66666667]
Adding one to all elements: [9 9 9 9]
Subtracting one from all elements: [1 1 1 1]You can also do other basic operations. Try them yourself in the Jupyter Notebook provided.
- Array indexing is the same as accessing an array element.
- You can access an array element by referring to its index number.
import numpy as np
arr1= np.array([3,2,3,4])
arr2= np.array([2,1,1,3])
arr3= np.array(['D','e','V','I','n','c','e','p','t'])
arr4= np.array([[1,2,3,4,5], [6,7,8,9,10]])
print(arr1[0]) # prints first element
print(arr1[-1]) # prints last element
print(arr2[2]) # prints third element
print(arr3[0]) # prints first element
print(arr4[1][3]) #prints 9
print(arr4[1,3]) # Or you can use this type Result:
3
4
1
D
9
9Array slicing is same as String Slicing so don't worry...
- Slicing in python means taking elements from one given index to another given index.
- We pass slice instead of index like this:
[start:end]. - You can also provide Step size as:
[start:end:step].
import numpy as np
arr1=np.array(['D','e','V','I','n','c','e','p','t'])
arr2=np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9])
#2-D Slicing
arr3=np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
print(arr1[:3]) # default is taken as 0
print(arr1[0:3])
print(arr1[3:]) # taken till the end
print(arr1[::2])
print(arr2[-4:-1])
print(arr2[::2]) # step size as 2
# 2-D Slicing
print(arr3[1,1:4])
print(arr3[0:2, 2])
print(arr3[0:2, 1:4])Result:
['D' 'e' 'V']
['D' 'e' 'V']
['I' 'n' 'c' 'e' 'p' 't']
['D' 'V' 'n' 'e' 't']
[6 7 8]
[1 3 5 7 9]
# Go over these results carefully they are bit tricky..
[7 8 9]
[3 8]
[[2 3 4]
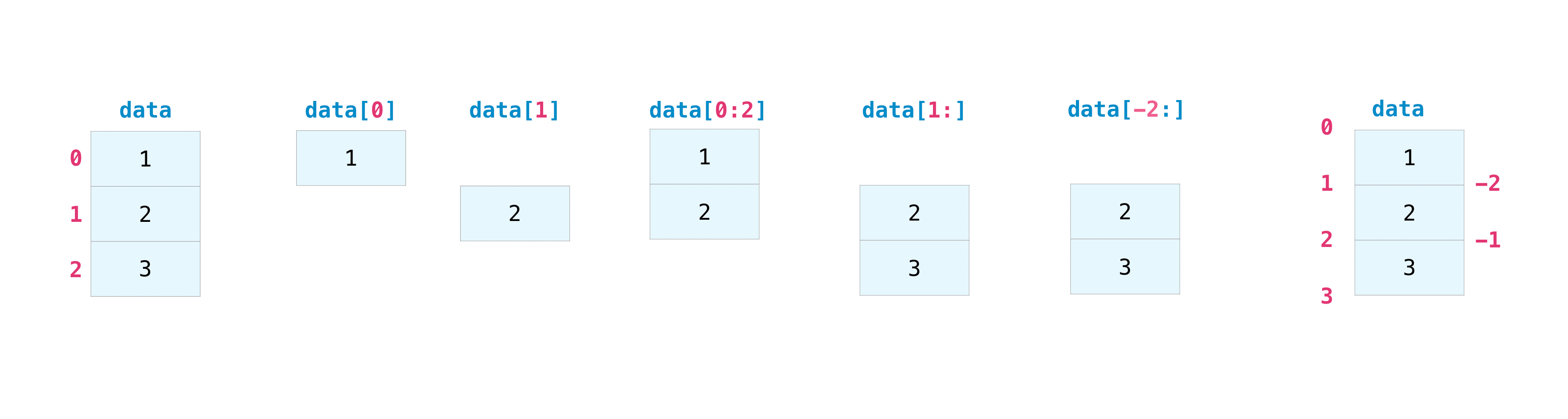
[7 8 9]] import numpy as np
data = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(data[1])
print(data[0:2])
print(data[1:])
print(data[-2:])Result:
2
[1 2]
[2 3]
[2 3]