| title |
|---|
Git / Rebasing |
Git / Rebasing
- 有兩種方法可以將其他 branch 的異動併入 -
merge跟rebase,前者將兩個 branch 的 endpoint 接在一起,所以會有一個新的 commit;後者則以另一個 commit/branch 為基礎 (rebase) 重新套用 (reapply/replay) changes (例如git rebase origin/master),也因此之後 merge 會走 fast-forward,結果就是 cleaner/linear history。 - Rebase 其實是打掉重練 (abandoning existing commits and creating new ones that are similar but different),只是新的 commit 跟原來的很像而已,如果你 push 了些東西,其他人 pull 下去做了些修改,中間你又做了一次 rebase 再重新 push (用
--force硬是覆寫遠端的 history),這個動作會讓其他人抓狂。 - 所以 rebase 跟 merge 要選哪一個? 這跟如何看待 commit history 有關 - "record of what actually happened" (有一堆 merge commits 又如何,那就是真實發生的事) 或 "story of how your project was made",所以只是選擇的問題。建議是只對 local changes 做 rebase,不要對已經 push 的 changes 做 rebase。
- 就 local changes 而言,最常見的狀況是同時有多個人在同一個 branch 上工作時,由於大家頻繁地 push & pull,很可能因為 three-way merge 而產生多餘的 commit,可以在
git pull後用git rebase(不用加其他參數) 重新順一下 history。
參考資料:
- Git - Rebasing #ril
-
Git 裡有 2 種方式可以整合 branch 間的 change --
merge跟rebase,這裡將說明 rebasing 的妙用,以及什麼情況不要用它。 -
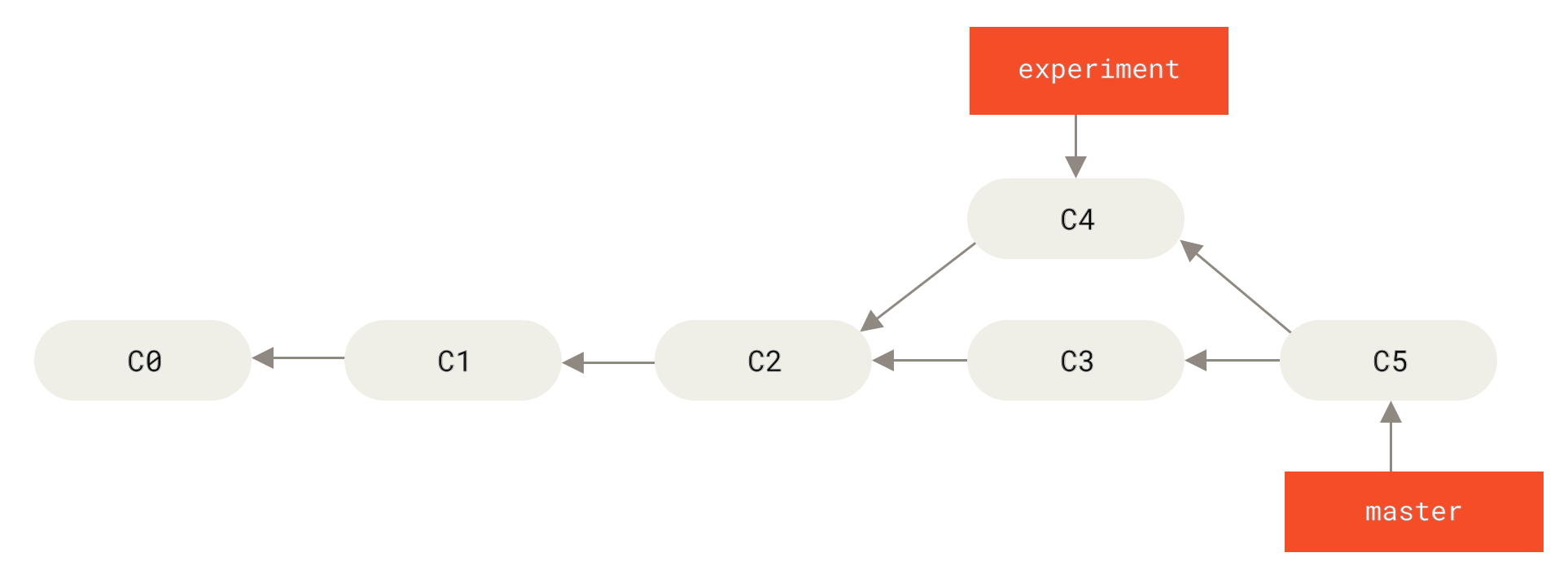
假設在 C2 分叉出 C3 (master) & C4 (experiment),此時
git merge(experiment 進 master) 會做 three-way merge -- two latest branch snapshots (C3, C4) 及 most recent common ancestor of the two (C2),進而產生一個新的 commit (C5) -- 將兩個 branch 的 endpoint 接在一起。 -
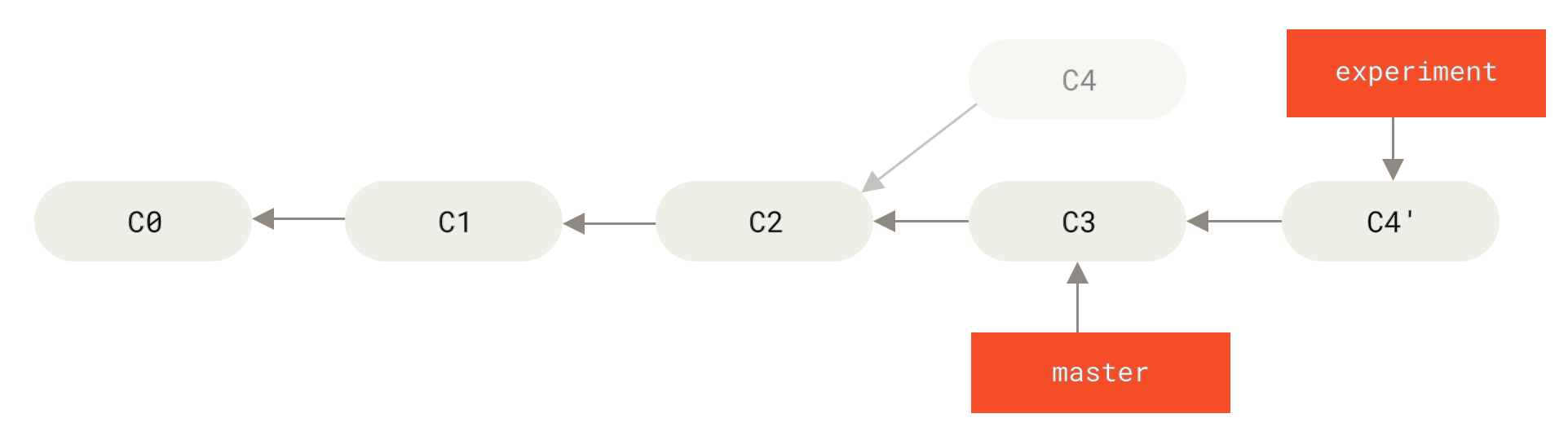
還有另一種做法 -- 把 C4 之於 C2 的 change,重新以 C3 為基礎重新套用 (reapply/replay) 一次,這就是 rebasing (
git rebase),也之所以新的 C4 (experiment) 要併進 C3 (master) 會是 fast-forward merge。$ git checkout experiment # C4 $ git rebase master # C3 First, rewinding head to replay your work on top of it.. # rebase == 改變目前 branch (C4) 的 base,從 C2 換成 C3 Applying: added staged command $ git checkout master $ git merge experiment # fast-forward merge -
就結果 (end product) 來看,merge 跟 rebasing 並沒有不同 (... is the same snapshot – it’s only the history that is different),但 rebasing 有 clean/linear history 的效果,看起來所有的 commit 是依序發生;若要貢獻的專案你沒有權限,發 PR 時可以先根據 target branch 做 rebase,這樣接受 PR 的人就不用做 integration work -- 單純的 fast-forward。
-
- Beginner’s Guide to Interactive Rebasing – Hacker Noon (2018-01-16) #ril
- Interactive rebasing can be used for changing commits in many ways such as editing, deleting, and squashing (擠壓).
- To tell Git where to start the interactive rebase, use the SHA-1 or index of the commit that immediately PRECEDES the commit you want to modify. 要用前一個 commit 當 rebase 的基礎,剛開始會不太習慣;得先花點時間在 log 裡翻找特定的 commit。
- During an interactive rebase, when Git pauses at a commit you TAGGED TO EDIT, the workflow is no different than a normal commit process — you stage files and then commit them. The only difference is you use the command
git commit --amendrather thangit commit. 前者是修改 commit (用git log看現在是基於哪個 commit 在修改),後者則會產生新的 commit。 - Interactive rebasing will create new SHA-1’s therefore it is best to use interactive rebasing on commits you have NOT PUSHED TO A REMOTE BRANCH.
- Using Git rebase on the command line - User Documentation #ril
- sjurba/rebase-editor: Simple terminal based sequence editor for git interactive rebase. 置換
sequence.editor#ril
手冊: