#FEWD - Layout
###Lesson #4 - Feb 10, 2016
"To the left to the left, everything you own in the box to the left."
- Beyonce (obviously singing about floats)
##Agenda
- Review
- Divs, Classes and IDs
- HTML5 Structural Elements
- Floats
- Lab Time
##Exit Tickets + Review
- More on
div
Answer: Our first topic tonight!
- If there's more than one way to structure/style a page, is there one way that's "best"?
Answer: It will depend on each specific project, the audience, the overall scope; as you develop your skills, you will refine a sense of balancing these needs and choosing the right direction for you codebase.
- DOM tree drawing and modifying
Answer: Keep practicing! Here's a nice interactive DOM tree example, and here's a great explanation of the Document Object Model.
##Exit Tickets + Review
- Can you have too many
divs?
Answer: Depending on the browser and the user's system, at a certain point, browsers may have a hard time rendering a lot of DOM elements (not just divs). But aside from performance issues (which, realistically, won't be much of an issue unless you're working with a HUGE dataset or a lot of interactive components), not really!
- What is the best way to remember how the box model affects your spacing, i.d "text-align"?
Answer: Practice + interacting with your projects via Chrome Inspector.
- Is there a "golden rule" when using margins and padding to style a page?
Answer: The basic "golden rule" to remember is that padding adds space INSIDE a box, while margin adds space OUTSIDE a box.
###What is a div?
A div is a type of tag that you used to group items together on a page.
###What are some common reasons for a div?
Most commonly, you will use divs to separate content structurally that needs to be grouped together and styled together; for example, consider the Relaxr landing page Assignment file.
##class & id
With classes and ids we can target specific elements on a page, so we can manipulate them uniquely.
##class & id
##class & id
###BEST PRACTICE ALERT! ###Never use spaces or capitalization in either a class or id value. ###Class and id attribute values should always be completely lowercased and "dash-delimited" (that means word breaks are denoted using a dash).
##class & id
DO:
<h1 class="title"><h1 class="main-title"><h1 class="main-header-title">
DON'T
<h1 class="Title"><h1 class="mainTitle">[This is called camel-casing and is used as formatting in other languages.]<h1 class="main header title">[This applies three classes to the h1.]
##class & id
####IDs are unique
####Classes are not unique
##class & id
When should you use them?
Classes are meant to be used to provide abstraction for many elements (because they are not unique); therefore anytime you are styling something that may share style declarations with another element, it's a good idea to use a class.
IDs are meant to be used to provide abstraction for one element (because it can only refer to a single, unique element); thus, use an ID where you want to individually call out something as unique (for example, a unique hero image background).
##class & id
How to select classes in CSS
.className
#idName
##HTML5 Structural Elements
Adding structure to HTML elements that are related to content layout.
- header
- section
- aside
- footer
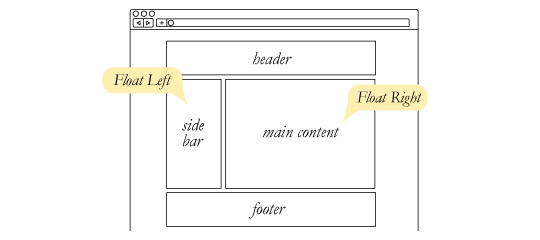
##Floats
Float is a CSS positioning property, used to layout a web page.
Note: Image from Chris Coyier's CSS-Tricks
##Resources
##Homework
- Assignment #2 - Relaxr Landing page
- Floats tutorial (not graded but good practice!)
###Please fill out the exit ticket before you leave